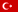
Live Broadcast Automation System
Platforms such as Netflix and Youtube have reached millions of users because the audience can watch the broadcasts they want with their own preferences, apart from a standard broadcast program and content. Many broadcasting organizations have added to their roadmaps to stop their traditional broadcasting activities over time. There are programs that reach thousands of viewers by broadcasting on a single tablet computer. At this stage, especially sports competition broadcasts have a special situation. For example, if we examine a broadcast of a match in our league, which was shot with six cameras, there is an operation in which approximately 20 people such as a director, technical director, slow motion operator, sound technician, cameramen and graphic operator work. The number of personnel in charge of more comprehensive broadcasts such as international matches can exceed 100. Our aim with the project is to develop a live broadcast automation system using technologies such as video / image processing technologies, artificial intelligence, network of objects.

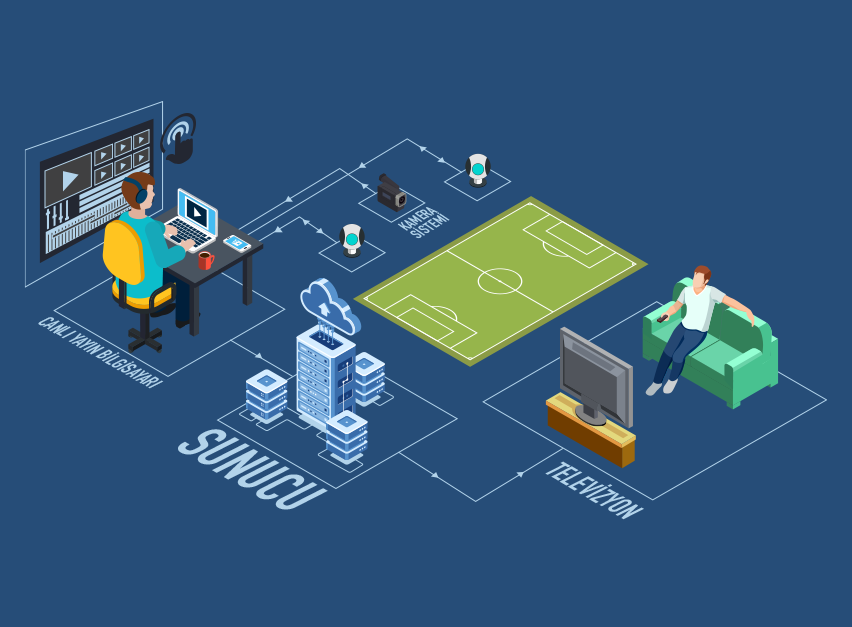
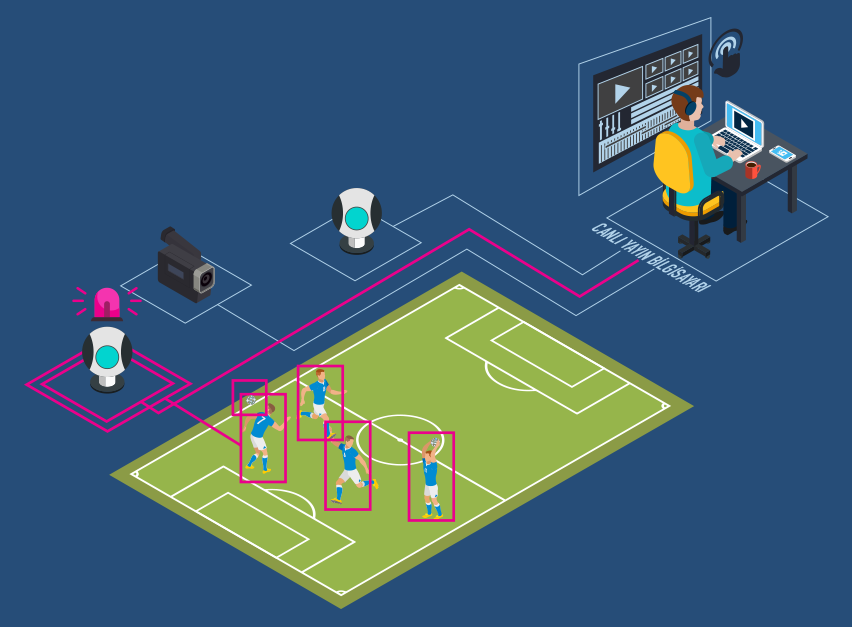
It is aimed to automate and disseminate a process that is still predominantly carried out by operators by using information and communication technologies. Artificial intelligence, machine vision, image and video processing that will take place in the live broadcast automation system that we aim to create operation performed by at least ten personnel in many different profiles such as director, picture selector, cameraman, technical director, graphic operator, sound technician, slow motion operator. technology will be able to be fulfilled with only a few personnel. Our long-term goal is to broadcast without an operator, provided that minimum broadcast quality is provided.
Artificial intelligence elements will be created and implemented for different sports branches. If we take a volleyball match as an example, if the team and player information about the match to be published before the match is available, it will be taken from the federation database, if not, it will be taken from the referee's table, including the first six formations. Cover page including team logos, line-up graphics with team rosters and top sixes, referee information will be given one after another. The game will be watched with the cameras to be placed on the field, and the system will produce suggestions or decide with artificial intelligence about which camera will be selected and broadcast at which moment with which angle and proximity value.
After certain positions, slow motions will still be prepared by the system. As soon as the score is given by the referee and entered by the table referee on the scoreboard, the score chart on the air will be updated, and the cameras will adjust themselves according to the team that will use the service. During the game, the active zone will be monitored by monitoring the athlete and ball movements with special filters (Kalman, etc.). As soon as any team takes a time-out, certain cameras will be able to adjust themselves to show the side of the court and the spectators. In this way, it is aimed to create branch-specific infrastructures.
Considering the example scenario, the detection and tracking of the active region, the image selection function, the slow motion display function include machine vision, image and video processing technologies. Artificial intelligence technologies will be applied to select cameras, automate or semi-automatic camera movements and optimize them according to sports branches.

Cevizlidere Caddesi 1/7
Çankaya / Ankara / Türkiye